Blogs & News
We are focus on automotive wiring harness & connectors technology.

Automotive High Voltage Connectors: Powering the Future of Electric Mobility
- Gvtong Electronic
- 48V board net connectors, Automated assembly connectors, automotive antenna connector, automotive coaxial connector, automotive data connector, automotive diagnostic connector, Automotive high - frequency connector, automotive High voltage connector, automotive high voltage connectors, automotive high voltage connectors company, automotive high voltage connectors manufacturer, automotive high voltage connectors market, automotive high voltage connectors supplier, automotive hybrid connector, automotive optical fiber connector, Automotive power distribution connector, Automotive temperature - resistant connector, automotive vibration - resistant, Automotive vibration - resistant connector, Automotive-grade AEC-Q200 connectors, Cost-effective automotive connectors, EV charging connectors, Fuel cell connectors, Halogen-free automotive connectors, In-cabin infotainment connectors Fuel cell connectors, Multi-variation connectors, OEM-specific connectors, Quick-fit automotive connectors, Recyclable material connectors, Redundant safety connectors, Thermal management connectors, V2X communication connectors, Wireless charging connectors
- No Comments
Automotive High Voltage Connectors: Powering the Future of Electric Mobility
Electric vehicles represent a paradigm shift from the traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles that have dominated the automotive landscape for over a century. Unlike ICE vehicles, which rely on low-voltage electrical systems (typically 12V or 24V), EVs and HEVs operate at much higher voltages—often between 400V and 800V or more. These elevated voltage levels are essential for efficiently powering electric motors, managing large battery packs, and enabling rapid charging capabilities.
High voltage connectors serve as the backbone of these electrical systems, facilitating secure and robust connections between key components. Far more than simple wiring accessories, these connectors are engineered to meet stringent performance, safety, and durability requirements. In this article, we will examine the intricacies of high voltage connectors, their role in the EV revolution, and how they are shaping the future of transportation.

What Is “High Voltage” in the Automotive Context?
To understand high voltage connectors, it’s essential to first define what “high voltage” means in the automotive world. In traditional vehicles, electrical systems operate at low voltages—12V for passenger cars and 24V for some commercial vehicles. These systems power accessories like lights, radios, and sensors but are insufficient for the demands of electric propulsion.
In contrast, electric and hybrid vehicles require significantly higher voltages to drive their motors and manage energy storage. For example:
- 400V systems are common in many current EVs, providing a balance of efficiency and practicality.
- 800V systems, used in high-performance EVs like the Porsche Taycan, enable faster charging and greater power delivery.
These elevated voltages reduce energy losses, improve efficiency, and allow for smaller, lighter wiring harnesses. However, they also introduce new challenges, such as the need for specialized connectors capable of handling high currents and voltages while maintaining safety and reliability.
Why High Voltage Connectors Are Essential
High voltage connectors are purpose-built to address the unique demands of EV electrical systems. Their primary functions include:
- Handling High Voltages: They must prevent electrical arcing and maintain insulation integrity under voltages far exceeding those of traditional vehicles.
- Carrying High Currents: EVs require substantial current to operate motors and charge batteries, and connectors must manage this without overheating or degrading.
- Ensuring Safety: With high voltages comes the risk of electric shock or system failure, so connectors incorporate features to protect users and components.
- Withstanding Harsh Conditions: Automotive environments expose connectors to extreme temperatures, vibrations, moisture, and chemicals, all of which they must endure.
Unlike low-voltage connectors, high voltage connectors are not optional accessories—they are critical to the operation and safety of electric vehicles.
Design and Construction of High Voltage Connectors
The engineering behind high voltage connectors is a sophisticated blend of electrical, mechanical, and materials science. Below are the key elements of their design:
- Insulation Materials
High voltage connectors rely on advanced insulating materials to prevent electrical breakdowns. Common materials include:
- Silicone rubber: Offers excellent flexibility and thermal resistance.
- Thermoplastic elastomers: Provide durability and dielectric strength.
- Thermoset plastics: Ensure stability under high temperatures and voltages.
These materials are chosen for their ability to insulate effectively while resisting wear over time.
- Contact Design
The metal contacts within the connector are designed to carry high currents with minimal resistance. Typically made from copper alloys, they are often plated with silver or gold to:
- Reduce electrical resistance.
- Prevent corrosion.
- Ensure reliable long-term performance.
- Sealing and Shielding
EVs operate in demanding environments, so connectors must be sealed against dust, water, and other contaminants. They also feature electromagnetic shielding to prevent interference with sensitive electronics, a critical consideration given the proximity of high voltage systems to control units.
- Locking Mechanisms
To prevent accidental disconnection—a potentially catastrophic event in a high voltage system—connectors incorporate robust locking features, such as:
- Latches: Simple yet effective manual locks.
- Screws: Provide a secure, tamper-resistant connection.
- Bayonet locks: Allow quick, reliable mating with a twist.
- Color Coding and Keying
High voltage connectors are typically orange, a universal indicator of high voltage in automotive applications. They also feature keying—physical shapes or notches—to ensure they can only connect to the correct counterpart, reducing the risk of errors during assembly or maintenance.
Safety Features and Standards
Safety is the top priority in high voltage systems, and connectors are designed with multiple layers of protection. They must comply with rigorous standards from organizations like the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) and the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE). Key safety features include:
- Touch-Proof Design
Connectors are engineered to prevent accidental contact with live electrical components. This is achieved through:
- Shrouds: Covers that shield exposed contacts.
- Recessed contacts: Positioning that makes it impossible to touch live parts.
- Interlock Systems
Many connectors include interlock circuits that monitor connection status. If a connector is disconnected or improperly mated, the system automatically disables the high voltage circuit to prevent hazards.
- High Voltage Interlock Loop (HVIL)
The HVIL is a safety mechanism that continuously checks the integrity of high voltage connections. If a fault is detected—such as a loose connector—the system shuts down to protect the vehicle and its occupants.
- Ingress Protection (IP) Ratings
High voltage connectors must meet high IP ratings (e.g., IP67 or IP68), ensuring they are:
- Dust-tight.
- Capable of withstanding water immersion, such as during heavy rain or flooding.
Applications in Electric Vehicles
High voltage connectors are deployed across multiple systems in EVs, each with specific requirements:
- Battery Pack Connections
The battery pack is the heart of an EV, and connectors link its modules to the power distribution system. These connectors must handle high currents and maintain reliability over thousands of charge-discharge cycles.
- Motor Connections
Electric motors require robust connections to the inverter and battery. High voltage connectors ensure efficient power delivery, minimizing losses and heat buildup.
- Charging Systems
During charging, connectors link the vehicle’s charging port to the battery pack. For fast-charging systems (e.g., DC fast chargers), they must support extremely high currents and voltages.
- Power Distribution
High voltage power is distributed to subsystems like HVAC units, onboard chargers, and auxiliary systems. Connectors ensure seamless integration across these components.
Challenges in High Voltage Connector Development
Designing high voltage connectors is not without its difficulties. Engineers face several challenges:
- Performance vs. Cost: Connectors must deliver top-tier performance while remaining affordable for mass production.
- Size and Weight: EVs prioritize efficiency, so connectors must be compact and lightweight without compromising capability.
- Higher Voltages: As systems move toward 800V and beyond, connectors must evolve to handle increased electrical stress.
- Durability: Connectors must last the lifespan of the vehicle—often 10-15 years—under harsh conditions.
Innovations Driving the Future
To meet these challenges, the industry is seeing exciting advancements in high voltage connector technology:
- Compact Designs
Smaller, lighter connectors save space and improve vehicle efficiency, a key focus as EVs become more mainstream.
- Higher Voltage Capabilities
New connectors are being developed to support voltages exceeding 800V, enabling ultra-fast charging and greater range.
- Advanced Materials
Innovations in insulation and contact materials enhance performance, durability, and resistance to environmental factors.
- Smart Connectors
Some connectors now integrate sensors to monitor temperature, current, and wear, allowing predictive maintenance and improved safety.
The Future of High Voltage Connectors
As electrification accelerates, high voltage connectors will play an increasingly vital role. Future trends include:
- Standardization
Standardized connector designs could streamline manufacturing, improve compatibility, and reduce costs across the industry.
- Wireless Power Transfer
Though still emerging, wireless charging could eventually reduce reliance on physical connectors for some applications, such as home charging.
- Sustainability
Eco-friendly materials and manufacturing processes are being explored to align with the broader sustainability goals of the EV industry.

Conclusion
Automotive high voltage connectors are far more than mere components—they are the lifelines of electric mobility. By ensuring the safe and efficient flow of power, they enable the performance, reliability, and safety that define modern electric vehicles. As the automotive industry continues its electrification journey, these connectors will evolve to meet new demands, driving innovation and shaping the future of transportation.
From battery packs to charging stations, high voltage connectors are the unsung heroes powering the EV revolution. Their development remains a critical focus for engineers and manufacturers, ensuring that the promise of electric mobility is realized safely and sustainably for generations to come.
For more about the best automotive high voltage connectors: powering the future of electric mobility, you can pay a visit to Gvtong at https://www.gvtong.net/ for more info.
Recent Posts
How to Diagnose and Repair Automotive Signal Connector Failures
How to Install and Maintain Low Pressure Automotive Connectors
Heat Shrink vs. Crimp: Choosing the Right 12V Car Wire Connector
Best 12V Automotive Wire Connectors for Reliable Electrical Connections
Tags
Recommended Products
-

GE Series-12-core cylinder connector
-

High voltage connector HV6-2PIN
-
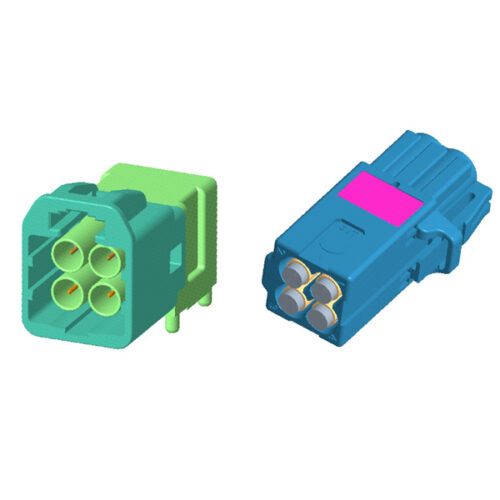
Automotive RF MINI FAKRA Four-Core Connector, Quad Port, PCB Through Hole, Right Angle, Plug, 50 Ohm
-

Wiring harness for medical equipments
-

High voltage connector (4 cores)
-
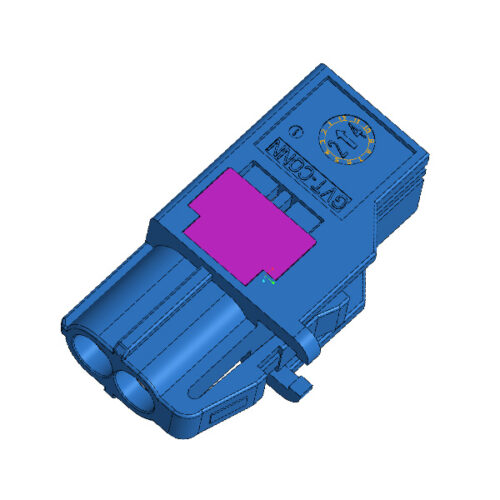
Automotive MINI Fakra High-Speed 2Pin Female To Fakra Male Z Code Connector
-

GE Series-10PIN Right Angle Connector Socket
-
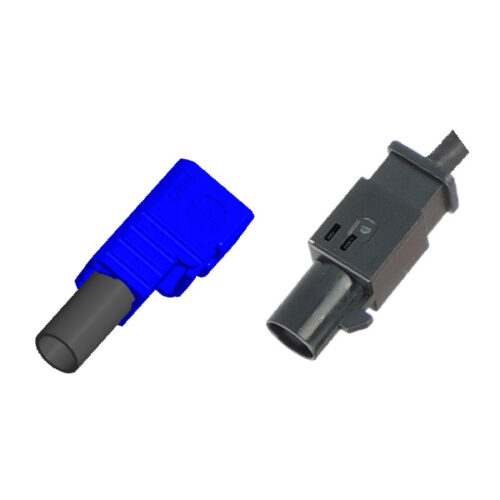
Automotive FAKRA Single Head Connector, Automotive Standard FAKRA Connectors
