Blogs & News
We are focus on automotive wiring harness & connectors technology.

Automotive Low Voltage Signal And Power Connectivity Solutions
- Gvtong Electronic
- Automotive Connector and Cable Products, automotive Low voltage connector, Automotive Low Voltage Connector China, Automotive Low Voltage Connector Manufacturer, Automotive Low Voltage Connector Supplier, automotive low voltage signal and power connectivity solutions, Automotive Low Voltage Wiring Harness, Automotive Power Supply solutions, Best automotive low voltage connectors, Low Voltage Differential Signaling LVDS Automotive, Low Voltage Signal and Power Connector Solutions, Low Voltage Signal Connector Solutions, Low Voltage Systems for Electric ATVs, Low Voltage Wiring Harness, Low Voltage Wiring Harness China, Low-Voltage Differential Signalling, Low-Voltage Electrical Test Connectors, Power Distribution in Automotive Systems
- No Comments
Automotive Low Voltage Signal And Power Connectivity Solutions
Introduction to Automotive Electrical Systems
In modern vehicles, the electrical system forms a complex network that powers a vast array of components, from critical systems like the engine control unit to convenience features such as the infotainment system. Traditionally, automotive electrical architectures have relied on a 12-volt system, classified as “low voltage” in contrast to the high-voltage systems (often exceeding 400 volts) found in electric and hybrid vehicles. Even in these advanced vehicles, low-voltage systems remain essential for auxiliary functions, such as lighting, sensors, and control modules. The reliability of these electrical systems is non-negotiable—failures can lead to operational malfunctions, safety risks, or complete vehicle breakdowns. Central to this reliability are the connectivity solutions that ensure seamless transmission of power and signals throughout the vehicle. These solutions include wiring harnesses, connectors, terminals, and other components, all engineered to endure the harsh automotive environment characterized by vibration, temperature extremes, and exposure to moisture. This article delves into the world of automotive low voltage signal and power connectivity solutions, exploring the technologies, challenges, and innovations that underpin the functionality of contemporary vehicles.
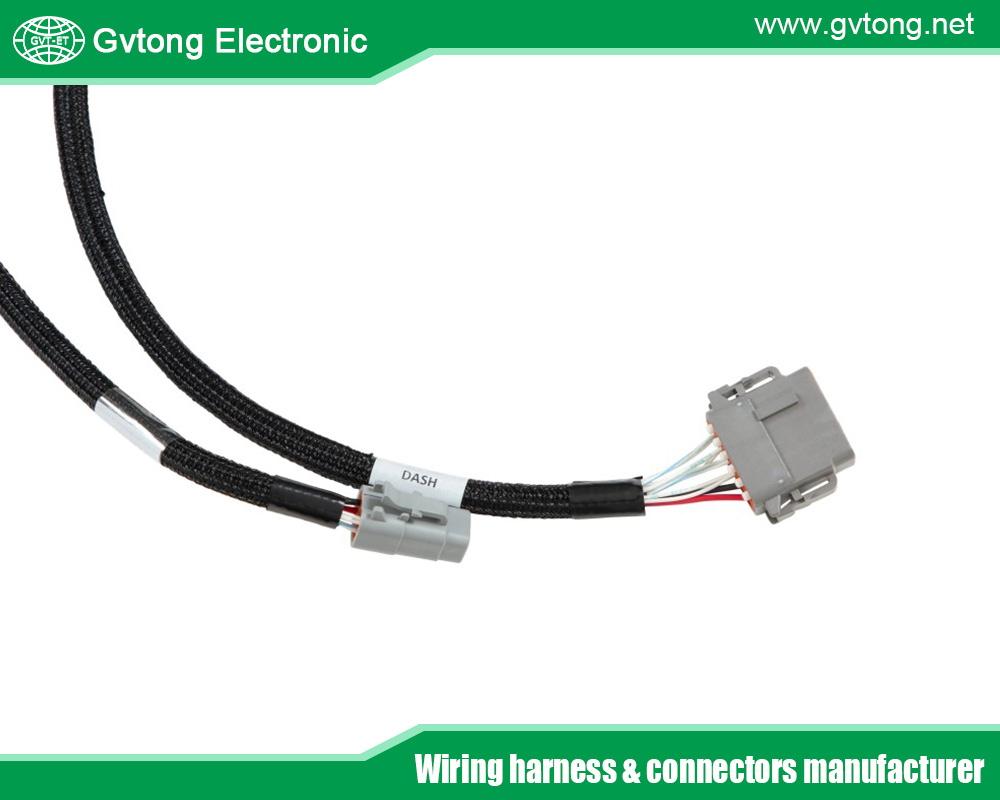
Low Voltage Power Connectivity Solutions
Overview and Importance
Power connectivity in automotive applications involves distributing electrical energy from the battery or alternator to various systems, such as headlights, fuel pumps, and ignition modules. The 12-volt system has long been the backbone of this distribution, delivering the necessary current to both essential and ancillary components. Ensuring consistent and reliable power delivery is a complex task given the demanding conditions vehicles face daily.
Key Components
Several components play pivotal roles in power connectivity:
Wiring Harnesses: These are organized bundles of wires that route power (and often signals) to different parts of the vehicle. Designed for flexibility and durability, they must resist abrasion, heat, and environmental degradation.
Connectors: These devices link sections of wiring harnesses or connect them to components. For power applications, connectors must support significant current loads while maintaining low resistance to prevent energy loss or overheating.
Fuses and Relays: Fuses safeguard circuits by breaking the connection during overcurrent events, while relays enable high-current devices to be controlled with low-current signals, enhancing efficiency and safety.
Power Distribution Modules: These units centralize fuses, relays, and sometimes connectors, streamlining the power distribution architecture.
Types of Power Connectors
Common connectors for power include:
Blade Connectors: Simple and cost-effective, used for low to medium current applications like interior lighting.
Ring Terminals: Ideal for high-current connections, such as battery terminals, offering a secure, bolted attachment.
Molex Mini-Fit Jr. or Similar: Used in various applications requiring compact, reliable power connections.
Challenges and Solutions
The automotive environment poses significant challenges to power connectivity:
Vibration: Constant movement can loosen connections. Locking mechanisms, such as clips or secondary locks, ensure connectors remain mated.
Temperature Extremes: Heat from the engine or cold from winter conditions can degrade materials. Connectors use high-temperature thermoplastics and heat-dissipating designs to cope.
Corrosion and Moisture: Exposure to water or salt can erode connections. Sealed connectors with gaskets or O-rings achieve high IP ratings (e.g., IP67) to prevent ingress.
Mechanical Stress: Wiring harnesses are routed to avoid sharp edges or high-heat zones, incorporating strain relief to prevent wire fatigue.
Materials also matter—copper alloys with tin or silver plating resist corrosion while maintaining conductivity. Additionally, features like Terminal Position Assurance (TPA) ensure terminals are fully seated, reducing the risk of intermittent connections. Rigorous testing, including vibration, thermal cycling, and corrosion resistance assessments, validates these solutions for automotive use.
Low Voltage Signal Connectivity Solutions
Overview and Importance
While power connectivity delivers energy, signal connectivity transmits data and control signals critical to vehicle operation. These signals range from analog sensor outputs (e.g., temperature readings) to digital communications between electronic control units (ECUs). With the proliferation of electronics in vehicles, reliable signal transmission is increasingly vital.
Types of Signals and Systems
Vehicles employ various signal types:
Analog Signals: Generated by sensors like throttle position or pressure sensors, requiring low noise and high accuracy.
Digital Signals: Used in data buses like CAN (Controller Area Network), LIN (Local Interconnect Network), or FlexRay for inter-module communication.
High-Speed Data: Found in infotainment or advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), necessitating higher bandwidths.
Connectors for Signal Transmission
Signal connectors prioritize integrity and include:
PCB Connectors: Link wiring harnesses to circuit boards in ECUs or modules.
Modular Connectors: Ruggedized versions of standards like RJ45 for automotive Ethernet.
FAKRA Connectors: Standardized for RF applications (e.g., GPS), with color-coding to prevent mismating.
Maintaining Signal Integrity
Signal corruption from electromagnetic interference (EMI) or noise is a major concern, given sources like ignition systems or electric motors. Solutions include:
Shielded Cables: Block external EMI for sensitive signals.
Twisted Pair Wiring: Reduces noise in differential signaling, common in CAN or Ethernet.
Filtering: Built-in filters or ferrite beads suppress high-frequency interference.
Impedance Matching: Essential for high-speed data to prevent signal reflections.
Miniaturization is another trend, with high-density connectors accommodating multiple signal lines in compact spaces. For instance, automotive Ethernet connectors support data rates up to 1 Gbps, balancing performance with durability.
Applications
Examples include connectors for airbag systems (requiring fail-safe reliability) or sensor networks in ADAS, where precision is critical. Modular systems allow scalability, enabling standardized connectors across vehicle platforms, which cuts costs and simplifies design.
Integration of Power and Signal Connectivity
Benefits of Integration
Combining power and signal transmission in a single connector or harness offers compelling advantages:
Space Savings: Reduces the size and weight of the electrical system.
Simplified Assembly: Fewer connectors lower the risk of installation errors.
Cost Efficiency: Decreases material and manufacturing expenses.
Hybrid Connectors
Hybrid connectors house both power and signal contacts, requiring careful design to avoid crosstalk or interference. Examples include:
Sensor Connectors: Deliver power and return signal data (e.g., oxygen sensors).
Actuator Connectors: Supply power and control signals to motors or solenoids.
Module Connectors: Provide power, ground, and multiple signal lines to ECUs.
Design Considerations
Key factors include:
Contact Arrangement: Separates power and signal lines to minimize interference.
Insulation: Prevents shorts or signal degradation between contacts.
Robust Housing: Protects against environmental stressors.
Emerging technologies like Power over Data Line (PoDL) transmit power and signals over the same wires, though this is less common in low-voltage automotive systems today.
Emerging Trends and Technologies
Impact of Electrification
Vehicle electrification increases the load on low-voltage systems, even in EVs with high-voltage batteries. This drives demand for robust connectors and efficient power distribution innovations.
Automotive Ethernet
The shift to high-speed data for infotainment and autonomy has popularized automotive Ethernet, requiring connectors that support gigabit speeds while enduring automotive conditions.
Wireless and Smart Solutions
While wireless connectivity (e.g., for keyless entry) is growing, wired solutions dominate for power and critical signals due to reliability. Smart connectors with diagnostics or identification features are emerging, aiding maintenance and troubleshooting.
Sustainability and Future Outlook
Sustainability pushes for recyclable materials and reduced resource use. Zonal architectures—dividing vehicles into electrical zones—may reshape harness and connector designs, enhancing modularity. The future promises continued innovation to meet rising performance and reliability demands.
Case Studies
Telematics Control Unit (TCU): Requires power and high-speed data connectors with EMI shielding for network connectivity.
Battery Management System (BMS): Uses compact hybrid connectors for low-voltage interfaces in EV battery packs.
Infotainment Systems: Employ integrated connectors for power, audio, and data, reducing wiring complexity.
ADAS Sensor Modules: High-density connectors ensure accurate signal transmission from multiple sensors.

Conclusion
Automotive low voltage signal and power connectivity solutions are the unsung heroes of vehicle reliability, enabling everything from basic functions to cutting-edge technologies. As electrification, autonomy, and connectivity reshape the industry, these solutions must evolve to meet new challenges. By blending robust engineering with innovative design, they ensure vehicles remain safe, efficient, and ready for the road ahead.
For more about automotive low voltage signal and power connectivity solutions, you can pay a visit to Gvtong at https://www.gvtong.net/low-voltage/ for more info.
Recent Posts
How to Diagnose and Repair Automotive Signal Connector Failures
How to Install and Maintain Low Pressure Automotive Connectors
Heat Shrink vs. Crimp: Choosing the Right 12V Car Wire Connector
Best 12V Automotive Wire Connectors for Reliable Electrical Connections
Tags
Recommended Products
-

Metal connector-3.6mm-3 core
-
Automotive FAKRA Connector – Board End, DC to 3GHz From RF Connectors And Cables Manufacturer In China
-

Photovoltaic connector – Wire end socket
-

GE Series-32-core Low Voltage Connector-Socket+Plug
-

GE Series-14-core three-row signal connector
-

Current sensor bracket
-

GH800 Series-3-core plastic high voltage connector
-

Energy storage wiring harness
